上下文工程的实现路径
Context Engineering
为什么需要Context Engineering
文章强调”Communication is all you need”的理念
- 与LLM的沟通很困难,且经常被低估
- 许多智能体错误的根本原因在于沟通问题
- Context Engineering正是解决这些沟通问题的关键
AI在应用中的表现,除了模型本身能力,更关键的是能否获取“有效且准确的context”。这里的context,不只是上下文,而是模型在特定任务下能获得的真实、相关的信息。
Context Engineering 是为Agent在执行任务的每个步骤中,精确地向上下文窗口填充恰当信息
构成
主要包含数据源的RAG、state History和Memory,然后通过Prompt Engineering来组织数据,构造模版渲染输出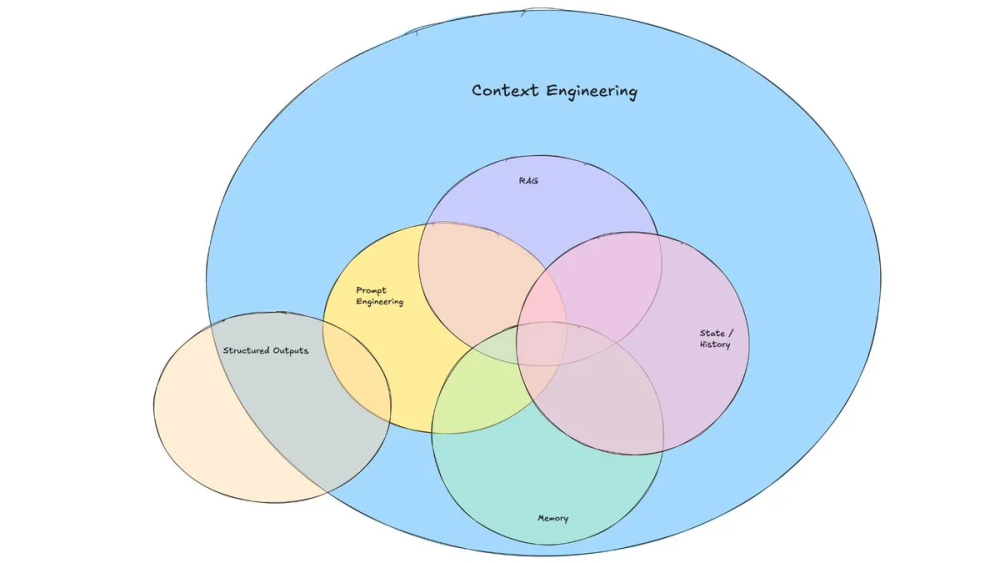
- Prompt Engineering: Instructions for how an agent should behave are clearly enumerated in the prompt,提示词、记忆、少样本示例、工具描述.
- Tool use: Making sure that if an agent needs access to external information, it has tools that can access it. When tools return information, they are formatted in a way that is maximally digestable for LLMs
- Short term memory: If a conversation is going on for a while, creating a summary of the conversation and using that in the future.
- Long term memory: If a user has expressed preferences in a previous conversation, being able to fetch that information.
- Retrieval: Fetching information dynamically and inserting it into the prompt before calling the LLM.
长上下文挑战
- 上下文中毒
比如当一次模型虚构了工具调用状态信息,被写入上下文时,在多轮循环中,模型可能会把错误信息误认为是事实反复引用,并执着于实现不可能或无关的目标,以至于后续每一步决策都在错误基础上前行,越走越偏。 - 上下文过长,情境干扰
当上下文过长,会导致模型注意力资源被稀释,过度关注上下文,忽略了原本通过训练获得的内容,输出质量下降。
虽然现在的大模型都已经支持百万级别的 token 上下文输入,但是 Gemini 2.5 的一份技术报告中指出,随着上下文超过10万个 token,大模型倾向于多步骤生成推理的长上下文,而非用于检索的长上下文。 - 多余信息过多,语境混淆
上下文中多余的内容也会干扰大模型的响应。以MCP工具调用为例,用过的朋友都知道,如果配置了数十个五花八门的MCP函数给大模型,每次调用时大模型要对数十个MCP做判断,调用工具决策的准确性会大幅下降。
伯克利今年6月发布的报告,显示大模型在引入函数调用或使用工具的时候,几乎所有大语言模型的性能都会比原始文本生成任务中有所下降,在多函数调用场景中,准确率显著低于单函数调用。 - 多个信息源,语境冲突
语境冲突常出现在多个Agent协作时,比如导航subAgentA说中山路往东,导航subAgentB说中山路要往西,大模型做决策时到底听谁的?
长上下文解决策略

1. Write Context(写入上下文)
将上下文保存在上下文窗口外部以帮助Agent执行任务
Scratchpads(草稿本)
- Agent可以做笔记并记住未来相关任务的信息
- 可以通过工具调用写入文件或保存在运行时状态对象中
- 例如:Anthropic的多Agent研究员将计划保存到Memory中
Memories(记忆)
- 跨多个会话记住信息
- Reflexion引入了每轮反思和重用自生成记忆的概念
- ChatGPT、Cursor、Windsurf都有基于用户-Agent交互自动生成长期记忆的机制
2. Select Context(选择上下文)
将上下文拉入上下文窗口以帮助Agent执行任务
从Scratchpad选择
- 通过工具调用读取或从运行时状态中选择性暴露
记忆memory选择
- 选择与当前任务相关的记忆
- 可以是少样本示例、指令或事实
- 使用嵌入或知识图谱进行记忆索引
工具选择
- 使用RAG对工具描述进行检索,获取最相关的工具
- 可以将工具选择准确率提高3倍
知识检索
- 代码Agent是大规模生产RAG的最佳例子
- 需要结合多种技术:grep/文件搜索、知识图谱检索、重排序等
3. Compress Context(压缩上下文)
仅保留执行任务所需的token
上下文总结
- Agent交互可能跨越数百轮对话
- Claude Code在超过95%上下文窗口时运行”auto-compact”
- 可以使用递归或分层总结策略
上下文修剪
- 使用硬编码启发式方法过滤上下文
- 例如从消息列表中删除较旧的消息

4. Isolate Context(隔离上下文)
将上下文分割以帮助Agent执行任务
多Agent
- 将上下文分散到子Agent中
- 每个Agent有特定的工具、指令和独立的上下文窗口
- OpenAI Swarm库的动机就是”关注点分离”

环境隔离
- HuggingFace的CodeAgent在沙箱中运行代码
- 将token密集的对象隔离在环境中

状态隔离
- 使用运行时状态对象隔离上下文
- 可以设计具有模式的状态对象(如Pydantic模型)
Context Schema 案例
Langgraph
- 将上下文划分为静态、动态和会存储的动态数据
https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/agents/context/ - 自定义state结构,state由框架控制在node之间传递
https://github.com/langchain-ai/langgraph/blob/main/docs/docs/tutorials/get-started/5-customize-state.md - 将长期记忆添加到state中
https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/how-tos/memory/add-memory/
Context-Engineering
- 将上下文划分为短期、长期和工作记忆,工作记忆比较特殊,是一些任务变量,我理解为一些kv
https://github.com/davidkimai/Context-Engineering/blob/main/00_foundations/03_cells_memory.md#advanced-techniques-memory-orchestration
ADK
官方文档: https://google.github.io/adk-docs/context/
上下文层次结构
🌟 Invocation (调用) - 最高级别包含多个agent的任务 - InvocationContext(根Context)
- 开始: 用户发送消息时创建
- 结束: 生成最终响应或Agent转移完成
- 管理: 由
runner.run_async()处理 - 状态共享:
session.state
1 | ├── Agent Call (Agent调用) - 中间级别 - InvocationContext(从父InvocationContext拷贝状态) |
核心功能特性
1. Maintaining State(状态维护)
用于在对话的多个步骤中记住详细信息,用于存储用户偏好、之前的计算结果、购物车项目等
session: Session- 当前会话对象(只读)- 包含
session.state:会话状态数据 - 包含
session.events:历史事件记录
- 包含
2. Passing Data(数据传递)
在步骤间共享发现或生成的信息
session: Session- 通过会话状态在步骤间传递数据user_content: Optional[types.Content]- 启动此次调用的用户内容(只读)end_invocation: bool- 控制是否结束当前调用的标志位
3. Accessing Services(访问服务)
与框架能力交互
3.1 Artifact Storage(工件存储)
artifact_service: Optional[BaseArtifactService]- 工件服务- 用于保存或加载与会话相关的文件或数据块(PDF、图像、配置文件等)
3.2 Memory(内存服务)
memory_service: Optional[BaseMemoryService]- 内存服务- 用于从过去的交互或连接到用户的外部知识源中搜索相关信息
3.3 Authentication(认证)
session_service: BaseSessionService- 会话服务- 管理认证状态和凭据
- 工具可以通过此服务请求和检索访问外部 API 所需的安全凭据
4. Identity and Tracking(身份和跟踪)
识别当前运行的代理和唯一标识请求-响应周期
invocation_id: str- 调用上下文的唯一ID(只读)- 用于日志记录和调试的唯一标识符
agent: BaseAgent- 当前代理(只读)- 通过
agent.name知道当前运行的代理
- 通过
branch: Optional[str]- 调用上下文的分支- 格式如
agent_1.agent_2.agent_3,用于多代理场景的追踪
- 格式如
5. Tool-Specific Actions(工具特定操作)
在工具内启用专门操作
live_request_queue: Optional[LiveRequestQueue]- 接收实时请求的队列active_streaming_tools: Optional[dict[str, ActiveStreamingTool]]- 当前调用的运行流式工具transcription_cache: Optional[list[TranscriptionEntry]]- 转录所需的缓存数据run_config: Optional[RunConfig]- 此次调用下实时代理的运行配置_invocation_cost_manager: _InvocationCostManager- 跟踪此次调用产生的各种成本的容器
Context Read & Write 案例
工具的索引和检索
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2506.01056
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2505.03275
使用mcp来查询可用的工具列表,进行一次过滤,而不是一次性将所有工具都传给大模型来判断使用哪个工具
Context and Inference
构建上下文提升推理效率(Prompt 与 KV Cache)
manus: https://manus.im/zh-cn/blog/Context-Engineering-for-AI-Agents-Lessons-from-Building-Manus, https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/A0D4wF1yv3nC3wye5Hcb4g
- 围绕KV Cache构建上下文:提示词前缀稳定、只追加
- 相同前缀带来kv cache命中率提升,所以把工具都拼到prompt前面

KV Cache原理:https://arxiv.org/pdf/2312.07104
使用掩码来屏蔽不使用的工具: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/619266782
Context as MCP
论文: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2507.07957
将滑动窗口等记忆模块也放到MCP里操作,实现主动检索机制。
主动检索机制
问题背景
- 传统内存增强系统(如Mem0、MemGPT)需要显式触发内存检索
- 语言模型默认使用参数化知识,可能过时或不正确
- 例如:用户之前说”Twitter的CEO是Linda Yaccarino”,几天后问”谁是Twitter的CEO?”
- 模型可能错误回答”Elon Musk”,因为对话历史中已无此信息
解决方案
系统分两个阶段运行:
- 主题生成: 代理根据输入生成当前主题
- 记忆检索: 利用主题从每个记忆组件中检索相关记忆
- 结果注入: 将检索结果注入系统提示符
检索策略
支持多种检索函数:
embedding_match- 嵌入匹配bm25match- BM25匹配string_match- 字符串匹配
优势
- 自动检索管道,无需显式用户提示
- 确保模型使用最新、个性化、上下文相关的信息
- 支持多样化和专门化的检索策略
参考
https://rlancemartin.github.io/2025/06/23/context_engineering/
https://blog.langchain.com/the-rise-of-context-engineering/
https://www.dbreunig.com/2025/06/22/how-contexts-fail-and-how-to-fix-them.html
https://github.com/langchain-ai/how_to_fix_your_context
一个面向PM的Context Engineering说明
https://x.com/PawelHuryn/status/1950126237562671313
https://www.productcompass.pm/p/context-engineering?utm_source=publication-search
claude是如何做上下文工程的:https://www.xiaohongshu.com/explore/6882005d000000001d00d53a?app_platform=android&ignoreEngage=true&app_version=8.92.0&share_from_user_hidden=true&xsec_source=app_share&type=normal&xsec_token=CBIAt7FwVT3rmjUCxeIUs-9z3euUYE-PTih9HgqFRJcJE=&author_share=1&xhsshare=CopyLink&shareRedId=ODc4Rjc2PDs2NzUyOTgwNjY1OTk4Rj1C&apptime=1753439829&share_id=c6e6707db94640ef8bd24b59ea1b466e&share_channel=copy_link
https://github.com/zilliztech/claude-context/blob/master/packages/core/src/context.ts
https://github.com/shareAI-lab/analysis_claude_code/blob/main/claude_code_v_1.0.33/stage1_analysis_workspace/docs/ana_docs/task_agent_analysis.md
https://baoyu.io/translations/decoding-claude-code
langgraph是如何做上下文工程的:https://blog.csdn.net/bugyinyin/article/details/149195239
manus是怎么做上下文工程的:https://manus.im/blog/Context-Engineering-for-AI-Agents-Lessons-from-Building-Manus
cline怎么做context engineering的
https://cline.bot/blog/how-to-think-about-context-engineering-in-cline
https://x.com/shao__meng/status/1957031656692543939
https://x.com/shao__meng/status/1957682039509118989
长期记忆
https://arxiv.org/pdf/2508.08997
https://github.com/agiresearch/A-mem
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/1888290059859514793
https://github.com/landing-ai/agentic-doc
上下文工程的链接
https://x.com/lenadroid/status/1943685060785524824
https://www.philschmid.de/context-engineering
https://blog.langchain.com/context-engineering-for-agents/